2023-02-13 オークリッジ国立研究所(ORNL)
 Oak Ridge National Laboratory researchers tested the performance of cellular shades in a two-story residential home in the Southeast and proved coverings with a honeycomb structure provide significant energy savings during winter and can potentially reduce carbon emissions. Credit: ORNL, U.S. Dept. of Energy
Oak Ridge National Laboratory researchers tested the performance of cellular shades in a two-story residential home in the Southeast and proved coverings with a honeycomb structure provide significant energy savings during winter and can potentially reduce carbon emissions. Credit: ORNL, U.S. Dept. of Energy
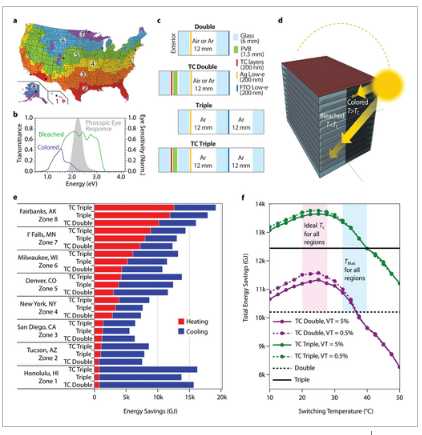
◆窓は熱を逃がすため、住宅のエネルギー需要を増加させますが、カバーリングによって断熱性を高めることができます。ある研究では、3つのシングルセルと2つのセルインセル構造のセルシェードと、一般的な横型ベネチアンブラインドの性能が比較されました。12月から3月までの2シーズン、アメリカ南東部の住宅で、2階の隣り合った同じ部屋の窓の上にシェードを設置しました。
◆「セルラーシェードを取り付けた部屋は、暖房エネルギーを最大24%節約することができました」と、ORNLのMahabir Bhandariは述べています。さらにエネルギーシミュレーションを行い、異なる気候帯でのシェードの性能を予測しました。「住宅にセルラーシェードが20%普及したと仮定すると、全国で300万トンまで炭素排出を削減できる可能性があります」。
<関連情報>
- https://www.ornl.gov/news/pulling-shades-energy-savings
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S036013232200823X
セルラーシェードの全国的な省エネの可能性:測定とシミュレーションによる研究 National energy savings potential of cellular shades: A measurement and simulation study
Niraj Kunwar, Mahabir Bhandari, Dragan C. Curcija
Building and Environment Available online :14 September 2022
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.buildenv.2022.109593
Highlights
- •Experimental testing of single-cell and cell-in-cell cellular shades in real house.
•Theoretical background of calculating characteristics of cellular shades.
•Comparison of the results from energy model with the experimental data.
•Calculation of national energy savings potential of cellular shades.
Abstract
Windows are major contributors to energy demand in residential homes because of their inferior thermal resistance compared with the opaque envelope, and sometimes from unwanted solar heat gain. Window attachments can help mitigate the energy demand by controlling the solar heat gains and enhancing window thermal resistance. Cellular shades have the potential of superior thermal performance compared with generic shades because of its honeycomb structure. In this study, the team analyzed the energy savings potential of cellular shades in residential homes via experimental testing for two heating seasons and energy simulations. Five shading devices—three single-cell and two double cellular/cell-in-cell shades—were used to compare the performance with generic horizontal venetian blinds using two nearly identical side-by-side rooms in a residential home. The experimental testing showed daily heating energy savings in the range of 17%–36% compared with the case without shades. The experimental testing data also exhibited improvements in thermal comfort when using cellular shades. Additionally, energy simulations were performed to evaluate the energy savings potential of the cellular shades using a residential prototype home, which demonstrated energy savings up to 9 kWh/m2/year in cold climates. The total site energy savings for heating and cooling from cellular shades was up to ∼9% for the home with a heat pump and up to ∼15% for a home with a gas furnace compared with cases without any shading devices. The energy savings at a national scale were up to 14.6 TWh assuming a 20% penetration rate in residential homes.