2023-08-22 バーミンガム大学
◆この研究は、低コストのセンサーを使用して空気品質をリアルタイムでモニタリングするための新しい方法論を開発し、空気汚染源の特定が難しいプロセスを改善しました。具体的な建設現場や地域の汚染ホットスポットで低コストセンサーを使用する可能性があり、環境へのポジティブな影響をサポートする方法として注目されています。
<関連情報>
- https://www.birmingham.ac.uk/news/2023/construction-sites-can-pinpoint-pollution-with-low-cost-sensing-tech-new-study
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41612-023-00424-0
汚染源センシングのための低コストセンサーを用いた包括的な空気品質管理に向けて Towards comprehensive air quality management using low-cost sensors for pollution source apportionment
Dimitrios Bousiotis,Gordon Allison,David C. S. Beddows,Roy M. Harrison & Francis D. Pope
npj Climate and Atmospheric Science Published:22 August 2023
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41612-023-00424-0
Abstract
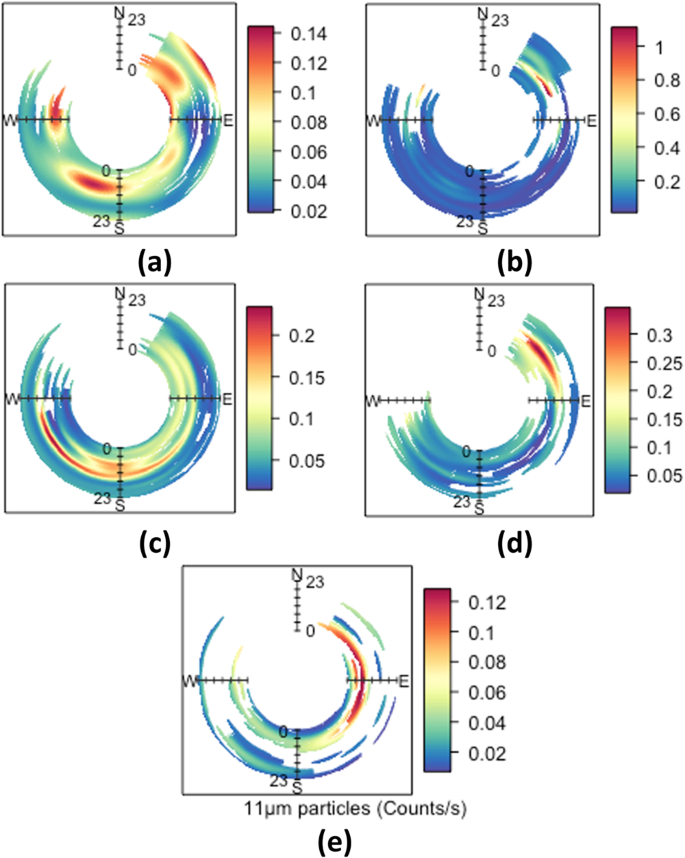
Successful air quality management and control not only requires measurements of air pollution levels. It also requires information on the sources of air pollution, and their relative magnitudes and importance, to plan and enact cost-effective control measures. This paper provides an important breakthrough towards the wider and more comprehensive use of source apportionment via low-cost techniques. Low-cost sensor measurements, along with the statistical methods of Positive Matrix Factorization (PMF) and k-means clustering, were able to successfully pinpoint and quantify the main sources of pollution in three regulatory important sites (a construction site, a quarry and a roadside). The anticipated levels of pollution, which were dependent on meteorological conditions and temporal variations, were assessed. The analysis provides information crucial for successful air quality management and control at a significantly lower cost than previously achieved. The strengths and weaknesses of the methodologies used are illustrated and discussed.