2025-03-14 産業技術総合研究所
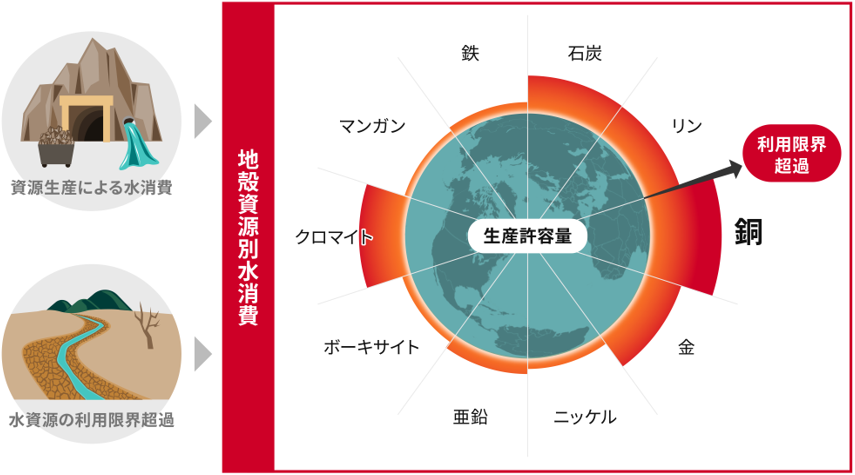
世界の地殻資源生産に伴う水消費と水資源の利用可能性から見た生産許容量の超過
<関連情報>
- https://www.aist.go.jp/aist_j/press_release/pr2025/pr20250314/pr20250314.html
- https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/science.adk5318
地域の水利用可能性に制約された地質資源生産 Geological resource production constrained by regional water availability
Kamrul Islam, Keitaro Maeno, Ryosuke Yokoi, Damien Giurco, […], and Masaharu Motoshita
Science Published:13 Mar 2025
Editor’s summary
Mineral production is key to our global economy, with new technologies creating higher demand for many minerals. However, large amounts of water are required for mining and processing, which could limit mineral production in some locations. Islam et al. evaluated these constraints using published data on mineral production and water requirements for different minerals, coupled with regional water-carrying capacities from a hydrologic model. They found that mineral production exceeds water resources in many regions because of high production or low water availability. Coal, iron, copper, and gold showed some of the highest overconsumption, coal because of its high production rates and the metals because they require more water to process. Water requirements for mineral production are expected to increase in the future. —Bianca Lopez
Abstract
Although the global economy requires geological resource mining, production has substantial environmental impacts, including the use of regional available water. In this study, we shed light on the global production capacity of 32 mined geological resources, considering regional water availability as a constraint. We found that current resource mining greatly exceeds regional water constraints for several, notably copper (37% of current production exceeds available water capacity) in 2010. Changing the location of production to regions of lower water stress would alleviate current exceedances of water constraints; however, considering economic factors shows that this is not always feasible. Future demand for geological resources is expected to require a considerable increase in water consumption. Considering the constraints of water resources in geological resource production is crucial for sustainability.



